What is OWASP?
The OWASP Open Web Application Security Project is a nonprofit foundation that works to improve the security of software. OWASP regularly update its list every 4 to 5 years.
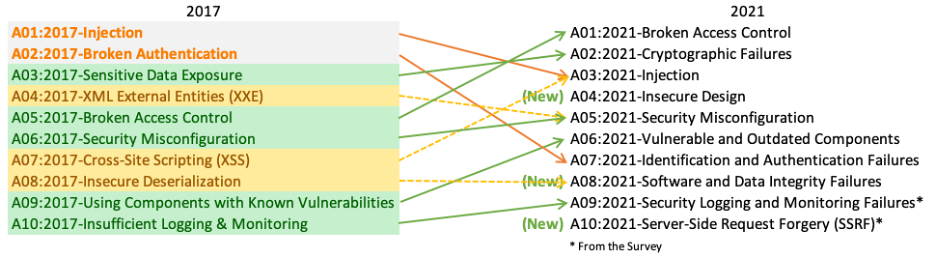
There are 10 most common web applications vulnerabilities which are listed in owasp top 10.
It was first updated in 2013 and then in 2017 and the latest release is 2021 which we are using now.
The OWASP Foundation is the source for developers and technologists to secure the web. OWASP
—
1. Broken Access Control
Broken access control is a flaw in the web application which occurs due to poor implementation of access control mechanisms that can be easily exploited.
This flaw allows attacker/unauthorised users to access the contents that they are not allowed to view, can perform unauthorised functions, and even an attacker can delete the content, or take over site administration.
Remediation
- Proper implementations of access control to the users.
- Delete any
inactive or unnecessary accounts.
- Shut down unnecessary
service and access point.
- Use
multi-factor authentication at all access points.
- Disable the web server directory listing.
2. Cryptographic Failures
This flaw previously was known as sensitive data exposures and it arises when web applications send any data in plain text, use outdated and insecure cryptographic algorithms, or weak crypto keys etc are called cryptographic failures.
General idea
This security threat occurs when web applications do not adequately protect sensitive information like credit card numbers, passwords, banking information, social security number, or any similar crucial data whose leak can be critical for the user.
This flaw in web applications can cause financial loss, access to victim’s accounts, blackmailing and ultimately decrease the trust in to brands.
Remediation
- Encrypt data while it is in transit and at rest.
- Use the most
up-to-date encryption techniques.
Turn off autocomplete on forms.- Reduce/minimize the size of the
data surface area.
- Use Strong adaptive and salted hashing functions when saving passwords.
3. Injection
An injection attack refers to untrusted data by an application that forces it to execute commands. Such data or malicious code is inserted by an attacker and can compromise data or the whole application.
The most common injection attacks are SQL injections, cross-site scripting (XSS), HTML injections, command injections, CCS injection, etc.
Remediation
- Separate the commands from the data.
- Data supplied by users must be validated, filtered, or sanitized.
- Use of a safe API that avoids the use of the interpreter altogether or uses parameterized queries
4. Insecure Design
This category of vulnerabilities is focused on the risks associated with flaws in design and architecture.
Remediation
- Development lifecycle with
AppSec professionals.
- Limit user and
service resource consumption.
- Implement
threat modelling for crucial authentication, access control, business logic, secure design patterns and key flows.
5. Security Misconfiguration
Security misconfiguration is a flaw in web applications and generally arises due to Default configurations, open ports, privileges, incorrect HTTP headers etc.
Remediation
- Improving security level of
potentials flaw application.
- Properly
configured permissions.
Default accounts/passwords be disabled or unchanged.Error messages should not display to users which contain sensitive information.- The
latest security features should be enabled.
- The
server, framework, libraries, or databases, security settings must be set to secure values.
- Remove the
unnecessary features, such as ports, services, pages, accounts, or privileges that are allowed or installed.
6. Vulnerable and Outdated Components
This category was previously known as Using Components with Known Vulnerabilities. Component vulnerabilities can arise when software is vulnerable, unsupported, out of date, or not upgraded platform, framework, and dependencies when patches come out.
Remediation
- Be aware of versions of
client-side and server-side components used.
- Perform
vulnerability Assessments to reduce attacks.
- Upgrade
platform, framework, and other dependencies.
7. Identification and Authentication Failures
This is the vulnerability that exists in the web application when the web application does not properly function related to identifications and authentications, like sessions management, password recovery, and other login credentials.
Because of this attackers are able to compromise passwords, security keys, or session tokens or assume to identities and permissions of other users.
Remediation
- Implement
multi-factor authentication (2FA)
- Do not deploy with
default credentials, especially for users with admin privileges.
- Enforce
strong passwords.
- Carefully
monitor failed login attempts.
- Use a secure session manager that generates
random, and time-limited session IDs.
- Never include
session IDs in URLs.
8. Software and Data Integrity Failures
This is a new category in the OWASP list that relates to vulnerabilities in software updates, critical data, and CI/CD pipelines whose integrity is not verified.
Code and infrastructure that do not guard against integrity violations are referred to as software and data integrity failures
For example, an application that relies on plugins, libraries, or modules from unverified and untrusted sources, repositories, or content delivery networks (CDNs) may be exposed to such a type of failure.
Remediation
- Use
digital signatures, or other similar measures.
- To protect the integrity of the code going through the
build and deploy processes, make sure your CI/CD pipeline includes adequate. segregation, configuration, and access control.
- Verify that
unsigned or unencrypted serialised data is not delivered to untrustworthy clients without an integrity check or digital signature to detect alteration or replay.
9. Security Logging and Monitoring Failures
It is one of the important vulnerabilities among OWASP Top 10 and was previously known as Insufficient Logging and Monitoring.
This flaw arises when organizations do not have proper logging and monitoring tools to insure all logs, detect suspicious activities and unauthorized access attempts. And all the alerts should be properly managed by security professionals.
Remediation
- Log all login,
access control, and server-side input validations failures.
- Logs must be in easily
readable format.
10. Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF)
Server-side request forgery issues arise when a web application does not validate the user-supplied URL when fetching a remote resource.
Or
SSRF is a web security flaw that allows an attacker to force a server-side application to send HTTP requests to any domain the attacker chooses.
Remediation
- Implement input validation.
- Use Regular Expressions (
RegEx).
- Only
accept the intended IP address format (IPv4 or IPv6).
Validate incoming Domain Names.
—
I have collected the above information from multiple articles and written
this post based on my understanding.
For more study on OWASP TOP 10, Please refer to the original post
Support me: If you like to support me, buy me a cup of coffee ☕
Follow me: @0xKayala | Satya Prakash