Internal audit is a process of evaluating and analyzing a company’s internal control systems, procedures, and processes to ensure they are operating effectively and efficiently. The primary objective of an internal audit is to provide independent assurance that a company’s operations are running as intended and to identify any areas of potential risk or inefficiencies.
An internal audit is conducted by an internal audit department or team within a company or organization. The internal audit team is typically independent of the areas they are reviewing and reports directly to the audit committee or board of directors.
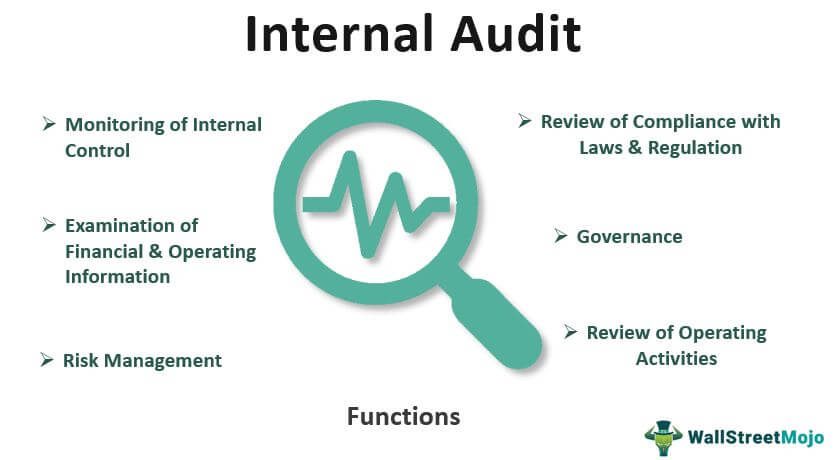
The main purposes of conducting an internal audit are:
Risk management: Internal audit helps identify potential risks to the organization and assesses the effectiveness of controls in place to mitigate those risks.
Compliance: Internal audit ensures that the organization is complying with all relevant laws, regulations, and internal policies and procedures.
Efficiency and effectiveness: Internal audit evaluates the effectiveness and efficiency of the organization’s operations, processes, and systems, and recommends improvements where necessary.
Governance: Internal audit assesses the effectiveness of the organization’s governance framework, including the board of directors and executive management.
Financial reporting: Internal audit evaluates the accuracy and completeness of financial reporting and helps ensure the integrity of financial information.
Overall, an internal audit provides an objective, independent assessment of an organization’s operations and provides recommendations for improvement, making it an essential tool for maintaining good governance, risk management, and operational effectiveness.
There are several advantages of conducting an internal audit within an organization. Here are some of the key benefits:
- Improved risk management: Internal audit helps identify potential risks to the organization and assesses the effectiveness of controls in place to mitigate those risks. This helps the organization to better manage and mitigate risks, reducing the likelihood of negative outcomes.
- Enhanced compliance: Internal audit ensures that the organization is complying with all relevant laws, regulations, and internal policies and procedures. This helps the organization avoid penalties, fines, and legal issues.
- Increased efficiency and effectiveness: Internal audit evaluates the effectiveness and efficiency of the organization’s operations, processes, and systems, and recommends improvements where necessary. This can help the organization to operate more efficiently, reduce costs, and improve overall performance.
- Improved governance: Internal audit assesses the effectiveness of the organization’s governance framework, including the board of directors and executive management. This helps the organization improve governance practices and ensure that decision-making processes are transparent and effective.
- Better financial reporting: Internal audit evaluates the accuracy and completeness of financial reporting and helps ensure the integrity of financial information. This can help the organization to make better financial decisions and maintain the confidence of stakeholders.
- Identification of opportunities: Internal audits may identify opportunities for improvement, innovation, and growth within the organization. This can help the organization to capitalize on these opportunities and achieve its strategic goals.
Overall, an internal audit provides an objective, independent assessment of an organization’s operations and helps the organization to identify and address issues and opportunities in a timely and effective manner.
Not performing an internal audit can have several risks for an organization, including:
Increased risk of fraud: Without regular internal audits, there is a greater risk of fraud going undetected. Fraudsters may take advantage of weak internal controls and processes to perpetrate fraudulent activities, leading to financial losses and reputational damage.
Increased risk of non-compliance: Failure to perform internal audits can lead to non-compliance with laws, regulations, and internal policies and procedures. This can result in fines, penalties, legal action, and reputational damage.
Inefficient operations: Without regular internal audits, there may be inefficiencies and waste in the organization’s operations and processes. This can lead to increased costs, lower productivity, and reduced competitiveness.
Poor governance: Internal audits provide an independent assessment of the effectiveness of the organization’s governance practices, including the board of directors and executive management. Failure to perform internal audits can lead to poor governance practices, with potentially negative consequences for the organization.
Inaccurate financial reporting: Without regular internal audits, there is a risk of inaccurate financial reporting. This can lead to poor decision-making, damage to the organization’s reputation, and potential legal and financial liabilities.
Overall, not performing internal audits can leave an organization vulnerable to a range of risks, including fraud, non-compliance, inefficiencies, poor governance, and inaccurate financial reporting. It is therefore important for organizations to conduct regular internal audits to identify and address potential issues before they become major problems.