In an increasingly digital world, the security of our digital assets has become a paramount concern. With the rise of cryptocurrencies and decentralized systems, securing the blockchain has become a pressing issue. The blockchain, a decentralized ledger that records transactions across multiple computers, is the foundation of many digital assets, from cryptocurrencies to smart contracts. However, its distributed nature also presents unique security challenges. This is why protecting the blockchain has become crucial for individuals and businesses alike. In this article, we will explore the importance of securing the blockchain and delve into the key measures that can be taken to safeguard digital assets. From encryption techniques to multi-factor authentication, we will explore the cutting-edge methods used to fortify the blockchain against cyber threats. Join us as we unpack the world of blockchain security and discover how it can help in protecting your valuable digital assets.
Don’t know what is blockchain then you can learn by spending 3 minutes here. Blockchain explained in 3 minutes
Importance of securing digital assets
As the use of blockchain technology continues to grow, so does the value of the digital assets stored on it. Cryptocurrencies, for example, have gained widespread adoption and are now considered valuable assets. Similarly, smart contracts, which automate and enforce contractual agreements, hold significant value in various industries. With the increasing value of these digital assets, the need for robust security measures becomes paramount.
One of the key advantages of the blockchain is its immutability. Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it becomes nearly impossible to alter or delete. However, this immutability also means that any security breach or vulnerability can have severe consequences. If a hacker gains unauthorized access to a user’s digital wallet or exploits a vulnerability in a smart contract, the consequences can be devastating.
Securing digital assets on the blockchain not only protects individuals from financial loss but also safeguards the integrity of the entire network. A single breach can erode trust in the technology and hinder its widespread adoption. Therefore, implementing effective security measures is crucial to maintain the trust and confidence of users in the blockchain.
Common threats and vulnerabilities in blockchain security
While the blockchain offers robust security features, it is not immune to threats and vulnerabilities. Like any other technology, the blockchain ecosystem is susceptible to various risks that can compromise the security of digital assets. Understanding these threats and vulnerabilities is essential to build a strong defense against potential attacks.
One of the most common threats in blockchain security is the 51% attack. In a 51% attack, a single entity or group of entities controls more than half of the computing power on the blockchain network. This allows them to manipulate transactions, reverse payments, and potentially double-spend cryptocurrencies. Another common vulnerability is the smart contract exploit, where hackers find vulnerabilities in the code and exploit them to gain unauthorized access or manipulate the contract’s logic. These threats highlight the need for robust security measures to protect digital assets on the blockchain.

Best practices for securing the blockchain
To fortify the blockchain against cyber threats, it is crucial to implement best practices for security. These practices encompass various aspects, from encryption techniques to access control mechanisms. By following these best practices, individuals and businesses can enhance the security of their digital assets on the blockchain.
Implementing strong encryption is a fundamental aspect of blockchain security. Encryption ensures that sensitive data is protected from unauthorized access. By encrypting data stored on the blockchain, even if a breach occurs, the stolen data remains unreadable and unusable. Additionally, encryption techniques can be applied to secure communication channels between blockchain nodes, further enhancing security.
Another best practice is the implementation of multi-factor authentication (MFA) and identity management protocols. MFA adds an additional layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of identification before accessing their digital assets. This can include a combination of passwords, bio-metric data, or hardware tokens. Identity management protocols help verify the authenticity of users and prevent unauthorized access to digital assets.
Regular security audits and penetration testing are also crucial for identifying vulnerabilities in the blockchain ecosystem. By conducting thorough security audits, businesses can proactively address any weaknesses and ensure that their digital assets are secure. Penetration testing involves simulating real-world attacks to identify potential security loopholes and vulnerabilities.
Implementing encryption and cryptography in blockchain security
Don’t know the role of Cryptographic Techniques in Blockchain? learn here, Exploring the Role of Cryptographic Techniques in Enhancing Blockchain Security
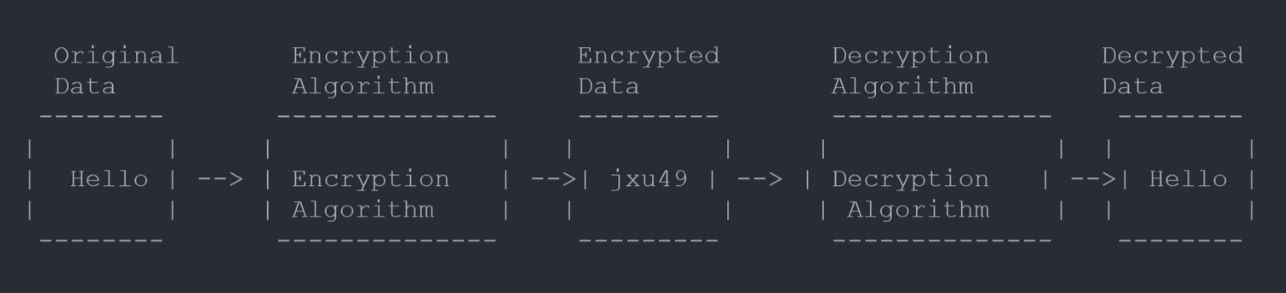
Encryption and cryptography play a vital role in securing the blockchain and protecting digital assets. Encryption ensures that data stored on the blockchain is unreadable without the proper decryption key. This prevents unauthorized access to sensitive information and adds an extra layer of security.
Cryptography, on the other hand, is used to ensure the integrity and authenticity of transactions on the blockchain. Digital signatures, for example, are cryptographic techniques used to verify the identity of transaction participants. By using public and private key pairs, digital signatures prevent unauthorized individuals from tampering with transactions.
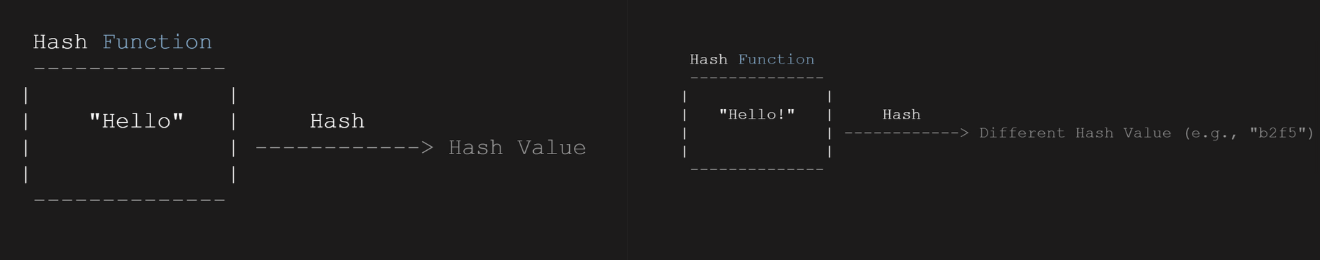
Another cryptographic technique used in blockchain security is hash functions. Hash functions generate unique and fixed-length hash values for each block on the blockchain. These hash values ensure the integrity of the blocks and provide a way to verify the authenticity of the entire chain. Any tampering with the data in a block would result in a different hash value, alerting participants to potential fraud.
Multi-factor authentication and identity management
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) and identity management protocols are essential for safeguarding digital assets on the blockchain. MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of identification before accessing their assets. This can include something the user knows (such as a password), something the user has (such as a hardware token), or something the user is (such as biometric data).
Identity management protocols help verify the authenticity of users and prevent unauthorized access to digital assets. These protocols ensure that only authorized individuals can interact with the blockchain and perform transactions. By implementing identity management, businesses can protect their digital assets from unauthorized access and potential fraud.
The role of smart contracts in blockchain security
Don’t know how the Smart Contracts works on Blockchain? learn here, Unveiling the Inner Mechanics of Smart Contracts on Ethereum
Smart contracts play a significant role in blockchain security. These self-executing contracts automatically enforce the terms and conditions of an agreement, eliminating the need for intermediaries. However, the code underlying smart contracts must be secure to prevent vulnerabilities and potential exploits.
Smart contract security involves rigorous testing and auditing of the code to identify potential vulnerabilities. The use of formal verification techniques can help ensure that the smart contract behaves as intended and is free from logical flaws. Additionally, implementing secure coding practices and adhering to industry standards can significantly enhance smart contract security.
Blockchain security audits and penetration testing
Regular security audits and penetration testing are essential for maintaining the security of the blockchain ecosystem. Security audits involve a comprehensive review of the blockchain infrastructure, protocols, and smart contracts to identify potential vulnerabilities. These audits can be conducted internally or by third-party security firms specializing in blockchain security.
Penetration testing, on the other hand, involves simulating real-world attacks to identify potential security loopholes and vulnerabilities. By conducting penetration tests, businesses can proactively address any weaknesses in their security measures and ensure that their digital assets are protected against potential threats.
Emerging trends and advancements in blockchain security
As the blockchain technology continues to evolve, so do the security measures designed to protect it. Several emerging trends and advancements in blockchain security show promise in enhancing the protection of digital assets on the blockchain.
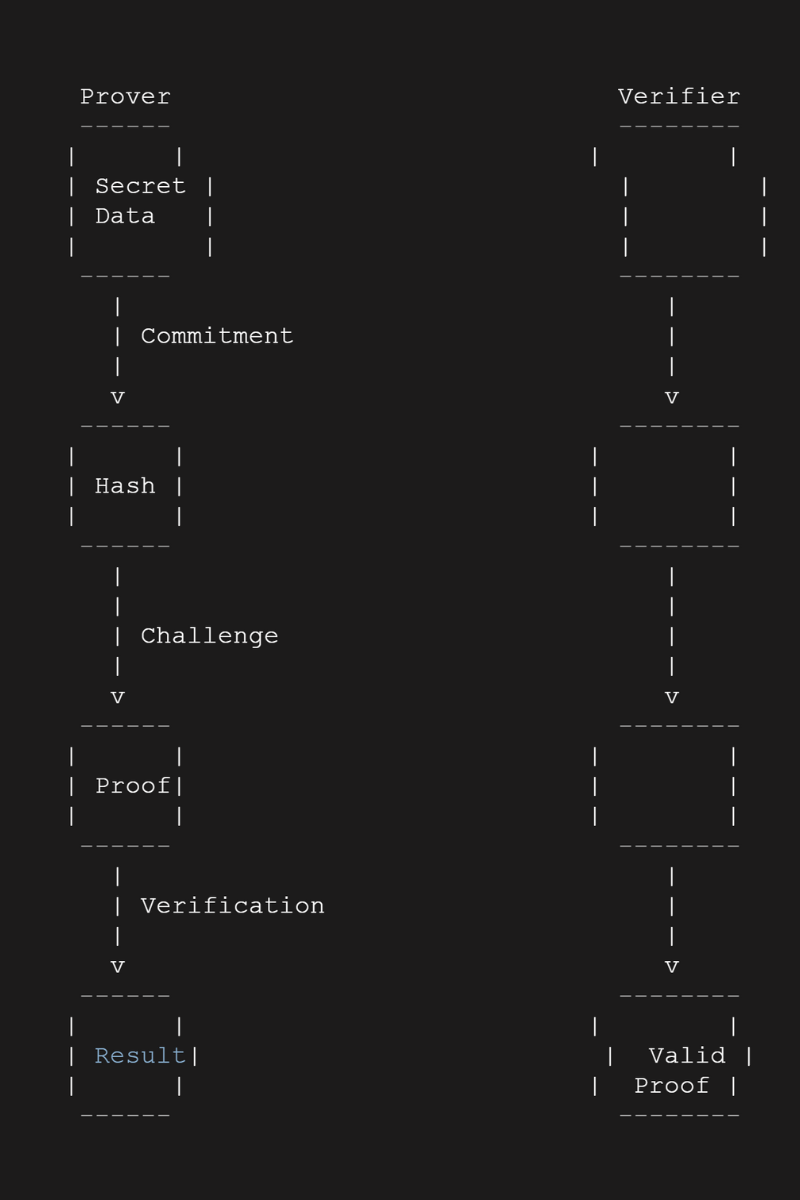
One such trend is the use of zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) to ensure privacy and confidentiality on the blockchain. ZKPs allow users to prove the validity of a statement without revealing any additional information. This can be utilized to protect sensitive data and transactions on the blockchain while maintaining the desired level of transparency.
Another advancement is the use of hardware security modules (HSMs) to safeguard the cryptographic keys used in blockchain transactions. HSMs provide secure storage and management of keys, ensuring that they cannot be tampered with or stolen. By utilizing HSMs, businesses can enhance the security of their digital assets and protect against unauthorized access.
Conclusion: The future of blockchain security
Securing the blockchain is crucial for protecting digital assets in an increasingly digital world. The distributed nature of the blockchain presents unique security challenges that must be addressed to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of transactions. By implementing encryption techniques, multi-factor authentication, and identity management protocols, individuals and businesses can fortify the blockchain against cyber threats.
Regular security audits, penetration testing, and adherence to best practices are essential for maintaining the security of the blockchain ecosystem. The use of advanced cryptographic techniques, such as zero-knowledge proofs and hardware security modules, shows promise in enhancing the protection of digital assets on the blockchain.