
The configuration of a dual boot is the best way to have a second operating system installed alongside a Windows partition. However, if to eliminate the second operating system, it is possible to see that the indicated partition is still remained, but the boot loader of the second operating system as well, in case if you decided to delete this partition. It is far beyond simply pointing out how to remove the unnecessary OS and, in addition, to clear the boot loader entries and expand your Windows space to take occupation of the released space.
Delete the Partition of the Second OS
To create an additional space which would suit the second operating system, delete the partition of the latter OS.
The first procedure is to remove the partition with the second OS using Disk Management tool.
- Open Disk Management: Press the ‘Windows’ button on your keyboard then press the ‘R’ button type ‘diskmgmt.msc’ and press the ‘Enter button’. This will open Disk Management utility in windows.
- Identify the OS Partition: So, find the partition that relates to the second operating system you want to install. It will most often a distinct partition having a different name in the file system (Linux
ext4 as this example).
- Delete the Partition: Using right mouse click, select on the second operating system (partition such as
ubuntu, debian and any other).
- Select Delete Volume. To destroy or erase the partition you need to confirm the action and the partition will be delete leaving unallocated space.
Note:
This action obliterate all data on the selected partition and hence ensure that you have backed all important data before partaking in this task.
Extend Windows Partition
You will notice that the second OS’s space is now unallocated, so you can incorporate the empty space into your Windows by extending your Windows partition.
- Right-click on the Windows Partition (C:: This is typically the primary partition where the Windows OS is located most of the time Even though people use partition to its conventional meaning, it is used here to mean a primary partition Fn = f(partition).
- Select “Extend Volume”: Use the suggested on screen wizard to select and incorporate the unallocated space to the existing Windows partition.
- Complete the Process: Once done, you will see that your system C: drive now has a larger capacity of storage space.
Clean Up the Boot Loader
When you start your computer, and the second OS is visible in the boot menu even after you deleted the partition. This remains because for example the boot loader entry will still be there.
- Access the EFI Partition:
- Power up your pc and type in the command prompt in the start search box, right click on Command Prompt and select “Run as an Administrator”. To do this, open the search bar and directly type cmd, right click it then click ‘Run as administrator’.
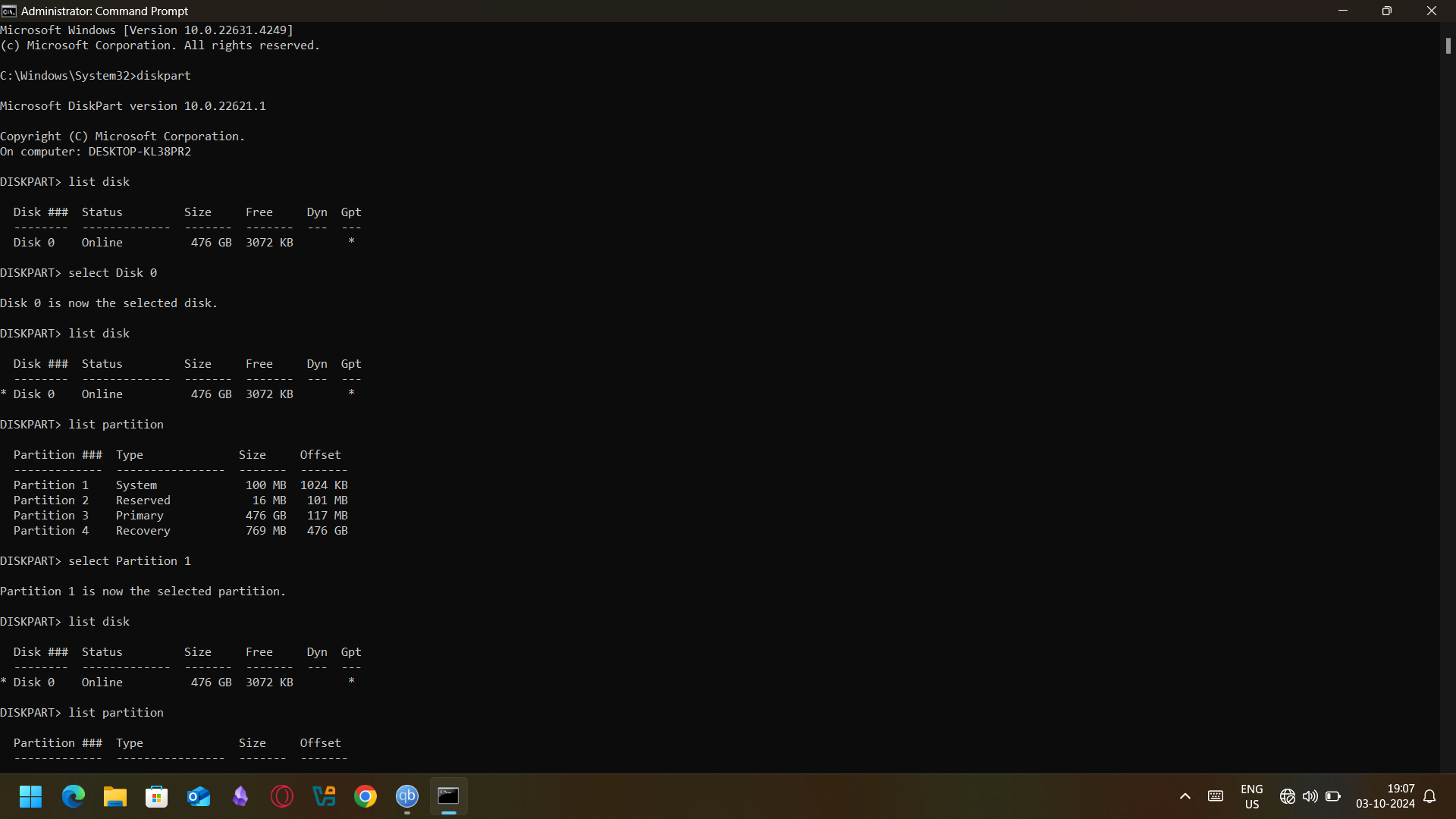
- Next, type diskpart and pressed the enter key. Enter into
list disk to check your disk number, for instance Disk 0 and then type select disk 0.
- To get a list of the partition, the ‘list partition’ option is used and for the selection of the system partition, there is usually ‘select partition 1’ if it is the small 100MB EFI one.
- To change the drive letter, type
assign letter=n and to exit DiskPart type exit.
- Remove the Boot Entries:
- Navigate to the EFI partition by typing
n: and pressing Enter.
- Specify the current directory as the EFI directory using the command
cd EFI.
- By opening the terminal and typing
dir, you should see directories that include Ubuntu, Debian or even Garuda depending with the OS you were using;
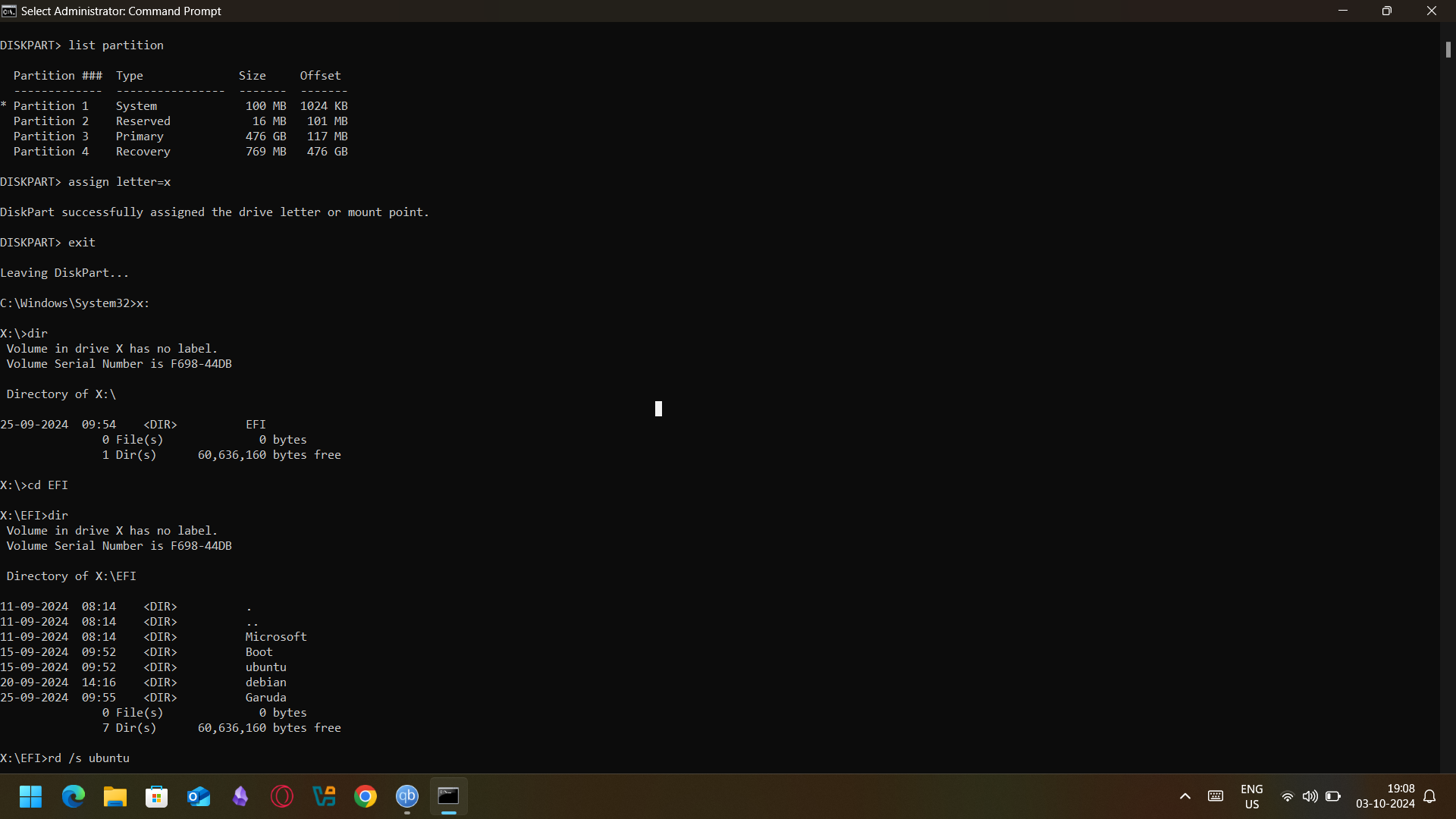
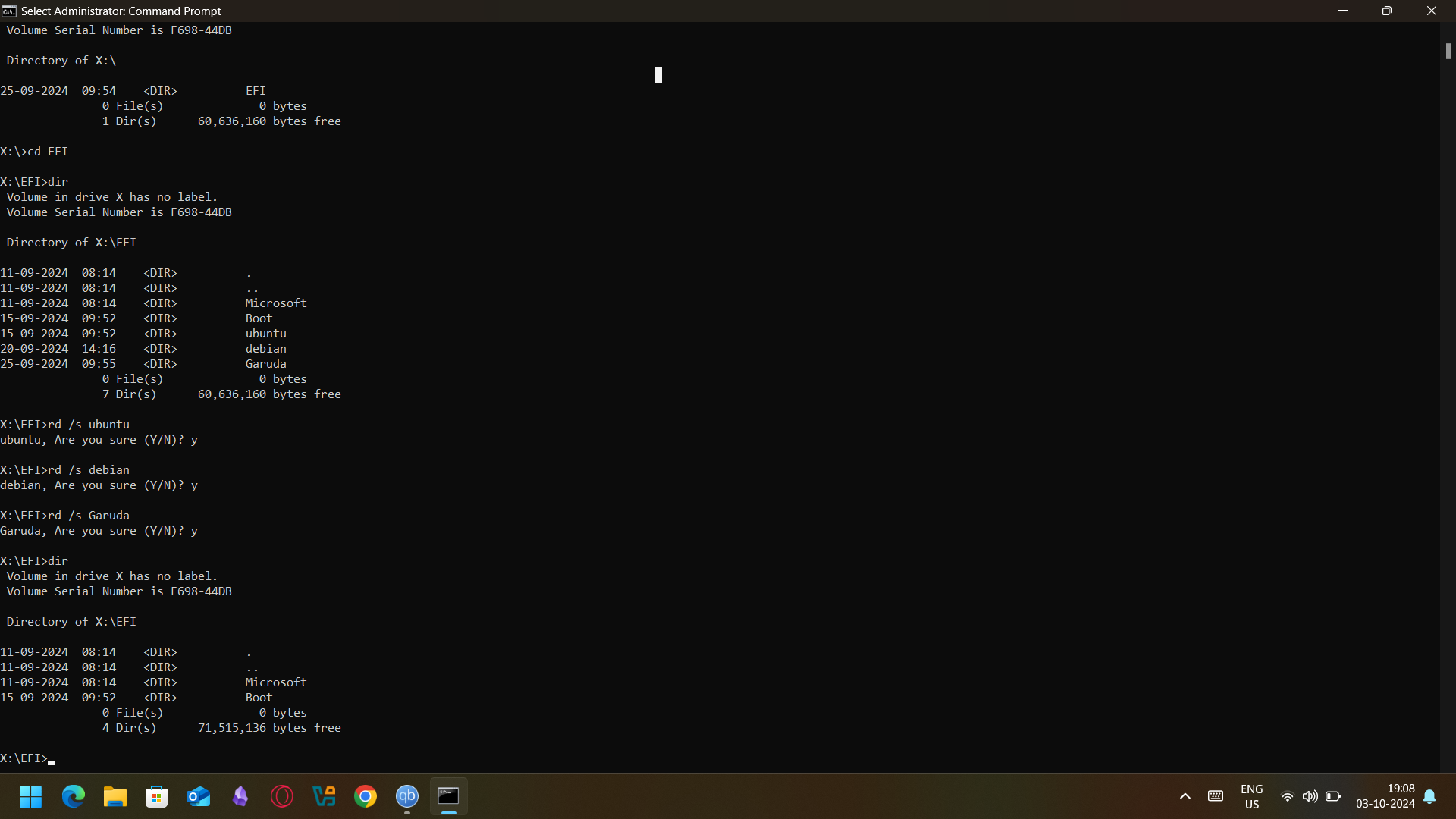
- Delete these using the rd command and enter the following commands
For example:
- `rd /s ubuntu`
- `rd /s debian`
- `rd /s Garuda`
- If that command does not working try this `Remove-Item -Path ubuntu -Recurse -Force`
- Clean the Boot Menu Using
bcdedit:
- It’s also important to note that you should now type
bcdedit in the Command Prompt window to view all the boot options.
- The command to delete it is
bcdedit /delete {identifier} Other changes were made only to replace {identifier} with the real identifier from the list.
This will cleaned the boot menu and the dual boot will no longer appear on the menu as shown below. Restart your computer and ensure that the boot menu no longer lists the removed OS. Your system should boot directly into Windows without any prompts for selecting an OS.